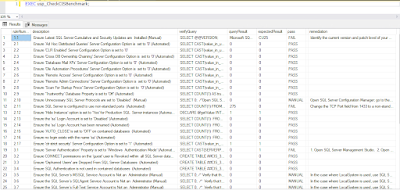
The beauty of this CIS benchmark automation created by me is pure SQL. It also allows you to add and change the verification rules.
USE [master]
GO
/****** Object: Table [dbo].[ErrorLog] Script Date: 22/04/2024 11:42:32 AM ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[ErrorLog](
[errorTime] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[errorMsg] [nvarchar](2048) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[ErrorLog] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_ErrorLog_errorTime] DEFAULT (getdate()) FOR [errorTime]
GO
USE [master]
GO
/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[error_handler_sp] Script Date: 22/04/2024 11:43:49 AM ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE OR ALTER PROC [dbo].[error_handler_sp] AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @errmsg nvarchar(2048),
@severity tinyint,
@state tinyint,
@errno int,
@proc sysname,
@lineno int
SELECT @errmsg = error_message(), @severity = error_severity(),
@state = error_state(), @errno = error_number(),
@proc = error_procedure(), @lineno = error_line()
IF @errmsg NOT LIKE '***%'
BEGIN
SELECT @errmsg = '*** ' + coalesce(quotename(@proc), '<dynamic SQL>') +
', Line ' + ltrim(str(@lineno)) + '. Errno ' +
ltrim(str(@errno)) + ': ' + @errmsg
END
INSERT ErrorLog (errorMsg) VALUES (@errmsg);
RAISERROR('%s', @severity, @state, @errmsg)
END
GO
USE [master]
GO
/****** Object: Table [dbo].[CISBenchmark] Script Date: 22/04/2024 11:45:49 AM ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[CISBenchmark](
[ruleNumber] [varchar](5) NOT NULL,
[description] [varchar](200) NOT NULL,
[verifyQuery] [nvarchar](4000) NOT NULL,
[expectedValue] [varchar](100) NULL,
[remediation] [nvarchar](4000) NULL,
[comparison] [varchar](10) NOT NULL,
[manual] [bit] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_CISBenchmark_resultLike] DEFAULT ('equal') FOR [comparison]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_CISBenchmark_manual] DEFAULT ((0)) FOR [manual]
GO
USE [master]
GO
/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[usp_CheckCISBenchmark] Script Date: 22/04/2024 11:47:13 AM ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE OR ALTER PROC [dbo].[usp_CheckCISBenchmark]
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
CREATE TABLE #CISResults (ruleNumber varchar(5), queryResult nvarchar(4000));
DECLARE @tblCurrQryResult table (queryResult nvarchar(4000));
DECLARE @ruleNumber varchar(5), @verifyQuery nvarchar(4000);
DECLARE cur CURSOR LOCAL FAST_FORWARD FOR
SELECT ruleNumber, verifyQuery FROM CISBenchmark ORDER BY ruleNumber;
OPEN cur
WHILE 1 = 1
BEGIN
FETCH cur INTO @ruleNumber, @verifyQuery;
IF @@FETCH_STATUS <> 0 BREAK;
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN TRAN
DELETE @tblCurrQryResult;
INSERT @tblCurrQryResult EXEC sp_executesql @verifyQuery;
INSERT #CISResults SELECT @ruleNumber, queryResult FROM @tblCurrQryResult;
COMMIT
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
IF XACT_STATE() <> 0 ROLLBACK;
EXEC error_handler_sp;
END CATCH
END
CLOSE cur;
DEALLOCATE cur;
WITH CTE AS (
SELECT R.ruleNumber, B.[description], B.verifyQuery, R.queryResult, B.expectedValue,
CASE
WHEN B.manual = 1 THEN 'MANUAL'
WHEN B.comparison = 'like' THEN
CASE WHEN R.queryResult LIKE '%'+B.expectedValue+'%' THEN 'PASS'
ELSE 'FAIL'
END
WHEN B.comparison = '>' THEN
CASE WHEN CAST(R.queryResult AS float) > CAST(B.expectedValue as float) THEN 'PASS'
ELSE 'FAIL'
END
WHEN B.comparison = '>=' THEN
CASE WHEN CAST(R.queryResult AS float) >= CAST(B.expectedValue as float) THEN 'PASS'
ELSE 'FAIL'
END
WHEN B.comparison = '<' THEN
CASE WHEN CAST(R.queryResult AS float) < CAST(B.expectedValue as float) THEN 'PASS'
ELSE 'FAIL'
END
WHEN B.comparison = '<=' THEN
CASE WHEN CAST(R.queryResult AS float) <= CAST(B.expectedValue as float) THEN 'PASS'
ELSE 'FAIL'
END
ELSE
CASE WHEN R.queryResult = B.expectedValue THEN 'PASS'
ELSE 'FAIL'
END
END
AS pass,
B.comparison,
B.remediation
FROM #CISResults AS R JOIN CISBenchmark AS B ON R.ruleNumber = B.ruleNumber
) SELECT ruleNumber, [description], verifyQuery, queryResult, expectedValue AS expectedResult, pass, comparison,
CASE pass WHEN 'PASS' THEN '' ELSE remediation END AS remediation
FROM CTE
ORDER BY CAST(LEFT(ruleNumber, CHARINDEX('.', ruleNumber)-1) AS int), CAST(RIGHT(ruleNumber, LEN(ruleNumber) - CHARINDEX('.', ruleNumber)) AS int);
END;
GO
USE [master]
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'1.1', N'Ensure Latest SQL Server Cumulative and Security Updates are
Installed (Manual)', N'SELECT @@VERSION;', N'CU25', N'Identify the current version and patch level of your SQL Server instances and ensure they
contain the latest security fixes.', N'like', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.1', N'Ensure ''Ad Hoc Distributed Queries'' Server Configuration Option is
set to ''0'' (Automated)', N'SELECT CAST(value_in_use AS bit) FROM sys.configurations WHERE [name] = ''Ad Hoc Distributed Queries'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''Ad Hoc Distributed Queries'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
14 | P a g e
EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.2', N'Ensure ''CLR Enabled'' Server Configuration Option is set to ''0''', N'SELECT CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''clr enabled'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''clr enabled'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.3', N'Ensure ''Cross DB Ownership Chaining'' Server Configuration Option is
set to ''0'' (Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''cross db ownership chaining'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''cross db ownership chaining'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.4', N'Ensure ''Database Mail XPs'' Server Configuration Option is set to ''0''
(Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''Database Mail XPs'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''Database Mail XPs'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.5', N'Ensure ''Ole Automation Procedures'' Server Configuration Option is
set to ''0'' (Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''Ole Automation Procedures'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''Ole Automation Procedures'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.7', N'Ensure ''Remote Admin Connections'' Server Configuration Option is
set to ''0'' (Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''remote admin connections'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''remote admin connections'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.8', N'Ensure ''Scan For Startup Procs'' Server Configuration Option is set to
''0'' (Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''scan for startup procs'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''scan for startup procs'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;
29 | P a g e
GO
EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.9', N'Ensure ''Trustworthy'' Database Property is set to ''Off'' (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1) AS trustworthyDb
FROM sys.databases
WHERE is_trustworthy_on = 1
AND name != ''msdb'';', N'0', N'ALTER DATABASE [<database_name>] SET TRUSTWORTHY OFF;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.11', N'Ensure SQL Server is configured to use non-standard ports
(Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1) FROM sys.dm_exec_connections WHERE local_tcp_port = 1433;', N'0', N'Change the TCP Port field from 1433 to a non-standard port', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.6', N'Ensure ''Remote Access'' Server Configuration Option is set to ''0''
(Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use AS bit) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''remote access'';', N'0', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''remote access'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;
GO', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.12', N'Ensure ''Hide Instance'' option is set to ''Yes'' for Production SQL
Server instances (Automated)', N'DECLARE @getValue INT;
EXEC master.sys.xp_regread
@rootkey = N''HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE'',
@key = N''SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQLServer\SuperSocketNetLib'',
@value_name = N''HideInstance'',
@value = @getValue OUTPUT;
SELECT @getValue;', N'1', N'1. In SQL Server Configuration Manager, expand SQL Server Network
Configuration, right-click Protocols for <InstanceName>, and then select
Properties.
2. On the Flags tab, in the Hide Instance box, select Yes, and then click OK to close the
dialog box. The change takes effect immediately for new connections.', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.14', N'Ensure the ''sa'' Login Account has been renamed (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.server_principals
WHERE sid = 0x01 AND [name] = ''sa'';', N'0', N'ALTER LOGIN sa WITH NAME = ''dbadmin'';', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.13', N'Ensure the ''sa'' Login Account is set to ''Disabled'' (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.server_principals
WHERE sid = 0x01
AND is_disabled = 0;', N'0', N'USE [master]
GO
DECLARE @tsql nvarchar(max)
SET @tsql = ''ALTER LOGIN '' + SUSER_NAME(0x01) + '' DISABLE''
EXEC (@tsql)
GO', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.16', N'Ensure no login exists with the name ''sa'' (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.server_principals
WHERE name = ''sa'';', N'0', N'USE [master]
GO
-- If principal_id = 1 or the login owns database objects, rename the sa
login
ALTER LOGIN [sa] WITH NAME = <different_name>;
GO
-- If the login owns no database objects, then drop it
-- Do NOT drop the login if it is principal_id = 1
DROP LOGIN sa', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.17', N'Ensure ''clr strict security'' Server Configuration Option is set to ''1''
(Automated)', N'SELECT
CAST(value_in_use as int) as value_in_use
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''clr strict security'';', N'1', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''clr strict security'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.15', N'Ensure ''AUTO_CLOSE'' is set to ''OFF'' on contained databases
(Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.databases
WHERE containment <> 0 and is_auto_close_on = 1;', N'0', N'ALTER DATABASE <database_name> SET AUTO_CLOSE OFF;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.1', N'Ensure ''Server Authentication'' Property is set to ''Windows
Authentication Mode'' (Automated)', N'SELECT CAST(SERVERPROPERTY(''IsIntegratedSecurityOnly'') AS int) AS [login_mode];
', N'1', N'1. Open SQL Server Management Studio.
2. Open the Object Explorer tab and connect to the target database instance.
3. Right click the instance name and select Properties.
4. Select the Security page from the left menu.
5. Set the Server authentication setting to Windows Authentication Mode.', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.2', N'Ensure CONNECT permissions on the ''guest'' user is Revoked within
all SQL Server databases excluding the master, msdb and tempdb
(Automated)', N'CREATE TABLE ##CIS_3_2 (dbname nvarchar(100), username nvarchar(100), permission nvarchar(100), state_desc nvarchar(100));
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ''USE [?];
INSERT ##CIS_3_2 SELECT DB_NAME() AS DatabaseName, ''''guest'''' AS Database_User,
[permission_name], [state_desc]
FROM sys.database_permissions
WHERE [grantee_principal_id] = DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_ID(''''guest'''')
AND [state_desc] LIKE ''''GRANT%''''
AND [permission_name] = ''''CONNECT''''
AND DB_NAME() NOT IN (''''master'''',''''tempdb'''',''''msdb'''');'';
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM ##CIS_3_2;
DROP TABLE ##CIS_3_2;', N'0', N'USE <database_name>;
GO
REVOKE CONNECT FROM guest;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.11', N'Ensure the public role in the msdb database is not granted access
to SQL Agent proxies (Automated)', N'USE [msdb];
SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM dbo.sysproxylogin spl
JOIN sys.database_principals dp
ON dp.sid = spl.sid
JOIN sysproxies sp
ON sp.proxy_id = spl.proxy_id
WHERE principal_id = USER_ID(''public'');', N'0', N'1. Ensure the required security principals are explicitly granted access to the proxy
(use sp_grant_login_to_proxy).
2. Revoke access to the <proxyname> from the public role.
USE [msdb]
GO
EXEC dbo.sp_revoke_login_from_proxy @name = N''public'', @proxy_name =
N''<proxyname>'';
GO', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'4.3', N'Ensure ''CHECK_POLICY'' Option is set to ''ON'' for All SQL
Authenticated Logins (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.sql_logins
WHERE is_policy_checked = 0
AND is_disabled <> 1;', N'0', N'/* list violated login(s) */
SELECT name
FROM sys.sql_logins
WHERE is_policy_checked = 0
AND is_disabled <> 1;
/* Set CHECK_POLICY = ON */
ALTER LOGIN [<login_name>] WITH CHECK_POLICY = ON;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.3', N'Ensure ''Orphaned Users'' are Dropped From SQL Server Databases
(Automated)', N'CREATE TABLE ##CIS_3_3 (username nvarchar(100), userid nvarchar(100));
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ''USE [?];
INSERT ##CIS_3_3
select p.name,p.sid
from sys.database_principals p
where p.type in (''''G'''',''''S'''',''''U'''')
and p.sid not in (select sid from sys.server_principals)
and p.name not in (
''''dbo'''',
''''guest'''',
''''INFORMATION_SCHEMA'''',
''''sys'''',
''''MS_DataCollectorInternalUser''''
);''
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM ##CIS_3_3;
DROP TABLE ##CIS_3_3;', N'0', N'USE <database_name>;
GO
DROP USER <username>;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.4', N'Ensure SQL Authentication is not used in contained databases
(Automated)', N'CREATE TABLE ##CIS_3_4 (name nvarchar(100));
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ''USE [?];
INSERT ##CIS_3_4 SELECT name AS DBUser
FROM sys.database_principals
WHERE name NOT IN (''''dbo'''',''''Information_Schema'''',''''sys'''',''''guest'''')
AND type IN (''''U'''',''''S'''',''''G'''')
AND authentication_type = 2;
'';
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM ##CIS_3_4;
DROP TABLE ##CIS_3_4;', N'0', N'SELECT name AS DBUser
FROM sys.database_principals
WHERE name NOT IN (''''dbo'''',''''Information_Schema'''',''''sys'''',''''guest'''')
AND type IN (''''U'''',''''S'''',''''G'''')
--AND authentication_type = 2;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'2.10', N'Ensure Unnecessary SQL Server Protocols are set to ''Disabled''
(Manual)', N'SELECT 0;
/*Open SQL Server Configuration Manager; go to the SQL Server Network Configuration.
Ensure that only required protocols are enabled.*/', N'0', N'Open SQL Server Configuration Manager; go to the SQL Server Network Configuration.
Ensure that only required protocols are enabled. Disable protocols not necessary.', N'equal', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.7', N'Ensure the SQL Server’s Full-Text Service Account is Not an
Administrator (Manual)', N'SELECT 0;
/*
Verify that the SQL Full-Text service account (in case of a local or AD account) and service SID are not
members of the Windows Administrators group.members of the Windows Administrators group.
*/', N'0', N'In the case where LocalSystem is used, use SQL Server Configuration Manager to change
to a less privileged account. Otherwise, remove the account or service SID from the
Administrators group. You may need to run the SQL Server Configuration Manager if underlying permissions had been changed or if SQL Server Configuration Manager was
not originally used to set the service account.', N'equal', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'4.1', N'Ensure ''MUST_CHANGE'' Option is set to ''ON'' for Newly Created SQL
Authenticated Logins (Manual)', N'SELECT 1; /* SELECT LOGINPROPERTY(name, ''IsMustChange'') FROM sys.sql_logins WHERE name = ''<new sql login>''; */', N'1', N'ALTER LOGIN <login_name> WITH PASSWORD = ''<new_password_value>'' MUST_CHANGE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'5.2', N'Ensure ''Default Trace Enabled'' Server Configuration Option is set to
''1'' (Automated)', N'SELECT CAST(value_in_use AS int)
FROM sys.configurations
WHERE name = ''default trace enabled'';', N'1', N'EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
EXECUTE sp_configure ''default trace enabled'', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
EXECUTE sp_configure ''show advanced options'', 0;
RECONFIGURE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'6.2', N'Ensure ''CLR Assembly Permission Set'' is set to ''SAFE_ACCESS'' for All
CLR Assemblies (Automated)', N'CREATE TABLE ##CIS_6_2 (name nvarchar(255));
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ''USE [?];
INSERT ##CIS_6_2
SELECT name
FROM sys.assemblies
WHERE is_user_defined = 1 AND permission_set_desc <> ''''SAFE_ACCESS'''';
'';
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM ##CIS_6_2;
DROP TABLE ##CIS_6_2;
', N'0', N'USE <database_name>;
GO
ALTER ASSEMBLY <assembly_name> WITH PERMISSION_SET = SAFE;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'7.1', N'Ensure ''Symmetric Key encryption algorithm'' is set to ''AES_128'' or
higher in non-system databases (Automated)', N'CREATE TABLE ##CIS_7_1 (name nvarchar(255));
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ''USE [?];
INSERT ##CIS_7_1
SELECT DB_NAME()
FROM sys.symmetric_keys
WHERE algorithm_desc NOT IN (''''AES_128'''', ''''AES_192'''', ''''AES_256'''')
AND DB_ID() > 4;
'';
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM ##CIS_7_1;
DROP TABLE ##CIS_7_1;', N'0', N'Refer to Microsoft SQL Server Books Online ALTER SYMMETRIC KEY entry:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/alter-symmetric-key-transact-sql', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.5', N'Ensure the SQL Server’s MSSQL Service Account is Not an
Administrator (Manual)', N'SELECT 0; /* Verify that the MSSQL service account (in case of a local or AD account) and service SID are not
members of the Windows Administrators group. */', N'0', N'In the case where LocalSystem is used, use SQL Server Configuration Manager to change
to a less privileged account. Otherwise, remove the account or service SID from the
Administrators group. You may need to run the SQL Server Configuration Manager if underlying permissions had been changed or if SQL Server Configuration Manager was
not originally used to set the service account.', N'equal', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.6', N'Ensure the SQL Server’s SQLAgent Service Account is Not an
Administrator (Manual)', N'SELECT 0;
/*
Verify that the SQL Agent service account (in case of a local or AD account) and service SID are not
members of the Windows Administrators group.
*/', N'0', N'In the case where LocalSystem is used, use SQL Server Configuration Manager to change
to a less privileged account. Otherwise, remove the account or service SID from the
Administrators group. You may need to run the SQL Server Configuration Manager if
underlying permissions had been changed or if SQL Server Configuration Manager was
not originally used to set the service account.', N'equal', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.8', N'Ensure only the default permissions specified by Microsoft are
granted to the public server role (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM master.sys.server_permissions
WHERE (grantee_principal_id = SUSER_SID(N''public'') and state_desc LIKE
''GRANT%'')
AND NOT (state_desc = ''GRANT'' and [permission_name] = ''VIEW ANY DATABASE'' and
class_desc = ''SERVER'')
AND NOT (state_desc = ''GRANT'' and [permission_name] = ''CONNECT'' and
class_desc = ''ENDPOINT'' and major_id = 2)
AND NOT (state_desc = ''GRANT'' and [permission_name] = ''CONNECT'' and
class_desc = ''ENDPOINT'' and major_id = 3)
AND NOT (state_desc = ''GRANT'' and [permission_name] = ''CONNECT'' and
class_desc = ''ENDPOINT'' and major_id = 4)
AND NOT (state_desc = ''GRANT'' and [permission_name] = ''CONNECT'' and
class_desc = ''ENDPOINT'' and major_id = 5);', N'0', N'USE [master]
GO
REVOKE <permission_name> FROM public;
GO', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.9', N'Ensure Windows BUILTIN groups are not SQL Logins (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.server_principals pr
JOIN sys.server_permissions pe
ON pr.principal_id = pe.grantee_principal_id
WHERE pr.name like ''BUILTIN%'';', N'0', N'USE [master]
GO
DROP LOGIN [BUILTIN\<name>]
GO', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'3.10', N'Ensure Windows local groups are not SQL Logins (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1)
FROM sys.server_principals pr
JOIN sys.server_permissions pe
ON pr.[principal_id] = pe.[grantee_principal_id]
WHERE pr.[type_desc] = ''WINDOWS_GROUP''
AND pr.[name] like CAST(SERVERPROPERTY(''MachineName'') AS nvarchar) + ''%'';', N'0', N'1. For each LocalGroupName login, if needed create an equivalent AD group containing
only the required user accounts.
2. Add the AD group or individual Windows accounts as a SQL Server login and grant it
the permissions required.
3. Drop the LocalGroupName login', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'7.2', N'Ensure Asymmetric Key Size is set to ''greater than or equal to 2048''
in non-system databases (Automated)', N'CREATE TABLE ##CIS_7_2 (name nvarchar(255));
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb ''USE [?];
INSERT ##CIS_7_2
SELECT DB_NAME()
FROM sys.asymmetric_keys
WHERE key_length < 2048
AND db_id() > 4;
'';
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM ##CIS_7_2;
DROP TABLE ##CIS_7_2;
', N'0', N'Refer to Microsoft SQL Server Books Online ALTER ASYMMETRIC KEY entry:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/alter-asymmetric-key-transactsql', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'4.2', N'Ensure ''CHECK_EXPIRATION'' Option is set to ''ON'' for All SQL
Authenticated Logins Within the Sysadmin Role (Automated)', N'SELECT SUM(cnt) FROM (
SELECT COUNT(*) cnt
FROM sys.sql_logins AS l
WHERE IS_SRVROLEMEMBER(''sysadmin'',name) = 1
AND l.is_disabled <> 1
AND l.is_expiration_checked <> 1
UNION ALL
SELECT COUNT(*) cnt
FROM sys.sql_logins AS l
JOIN sys.server_permissions AS p
ON l.principal_id = p.grantee_principal_id
WHERE p.type = ''CL'' AND p.state IN (''G'', ''W'')
AND l.is_disabled <> 1
AND l.is_expiration_checked <> 1
) AS T;', N'0', N'/* 1. List violated logins */
SELECT l.[name], ''sysadmin membership'' AS ''Access_Method''
FROM sys.sql_logins AS l
WHERE IS_SRVROLEMEMBER(''sysadmin'',name) = 1
AND l.is_expiration_checked <> 1
UNION ALL
SELECT l.[name], ''CONTROL SERVER'' AS ''Access_Method''
FROM sys.sql_logins AS l
JOIN sys.server_permissions AS p
ON l.principal_id = p.grantee_principal_id
WHERE p.type = ''CL'' AND p.state IN (''G'', ''W'')
AND l.is_expiration_checked <> 1;
/* 2. Set CHECK_EXPIRATION = ON */
ALTER LOGIN [<login_name>] WITH CHECK_EXPIRATION = ON;', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'5.1', N'Ensure ''Maximum number of error log files'' is set to greater than or
equal to ''12'' (Automated)', N'DECLARE @NumErrorLogs int;
EXEC master.sys.xp_instance_regread
N''HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE'',
N''Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\MSSQLServer'',
N''NumErrorLogs'',
@NumErrorLogs OUTPUT;
SELECT ISNULL(@NumErrorLogs, -1) AS [NumberOfLogFiles];', N'12', N'EXEC master.sys.xp_instance_regwrite
N''HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE'',
N''Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\MSSQLServer'',
N''NumErrorLogs'',
REG_DWORD,
<NumberAbove12>;', N'>=', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'5.3', N'Ensure ''Login Auditing'' is set to ''failed logins'' (Automated)', N'SELECT ''Failed logins only'';', N'Failed logins only', N'1. Open SQL Server Management Studio.
2. Right click the target instance and select Properties and navigate to the Security
tab.
3. Select the option Failed logins only under the Login Auditing section and click OK.
4. Restart the SQL Server instance.', N'equal', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'5.4', N'Ensure ''SQL Server Audit'' is set to capture both ''failed'' and
''successful logins'' (Automated)', N'SELECT COUNT(1) FROM (
SELECT DISTINCT
S.name AS ''Audit Name''
, CASE S.is_state_enabled
WHEN 1 THEN ''Y''
WHEN 0 THEN ''N'' END AS ''Audit Enabled''
, S.type_desc AS ''Write Location''
, SA.name AS ''Audit Specification Name''
, CASE SA.is_state_enabled
WHEN 1 THEN ''Y''
WHEN 0 THEN ''N'' END AS ''Audit Specification Enabled''
, SAD.audit_action_name
, SAD.audited_result
FROM sys.server_audit_specification_details AS SAD
JOIN sys.server_audit_specifications AS SA
ON SAD.server_specification_id = SA.server_specification_id
JOIN sys.server_audits AS S
ON SA.audit_guid = S.audit_guid
WHERE SAD.audit_action_id IN (''CNAU'', ''LGFL'', ''LGSD'')
) AS T;', N'3', N'1. Expand the SQL Server in Object Explorer.
2. Expand the Security Folder
3. Right-click on the Audits folder and choose New Audit...
4. Specify a name for the Server Audit.
5. Specify the audit destination details and then click OK to save the Server Audit.
6. Right-click on Server Audit Specifications and choose New Server Audit
Specification...
7. Name the Server Audit Specification
8. Select the just created Server Audit in the Audit drop-down selection.
9. Click the drop-down under Audit Action Type and select AUDIT_CHANGE_GROUP.
10. Click the new drop-down Audit Action Type and select FAILED_LOGIN_GROUP.
11. Click the new drop-down under Audit Action Type and select
SUCCESSFUL_LOGIN_GROUP.
12. Click OK to save the Server Audit Specification.
13. Right-click on the new Server Audit Specification and select Enable Server Audit
Specification.
14. Right-click on the new Server Audit and select Enable Server Audit.', N'equal', 0)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[CISBenchmark] ([ruleNumber], [description], [verifyQuery], [expectedValue], [remediation], [comparison], [manual]) VALUES (N'6.1', N'Ensure Database and Application User Input is Sanitized (Manual)', N'SELECT 0; /* Check with the application teams to ensure any database interaction is through the use of
stored procedures and not dynamic SQL. Revoke any INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE privileges
to users so that modifications to data must be done through stored procedures. Verify that
there''s no SQL query in the application code produced by string concatenation.*/', N'0', N'The following steps can be taken to remediate SQL injection vulnerabilities:
• Review TSQL and application code for SQL Injection
• Only permit minimally privileged accounts to send user input to the server
• Minimize the risk of SQL injection attack by using parameterized commands and
stored procedures
• Reject user input containing binary data, escape sequences, and comment
characters
• Always validate user input and do not use it directly to build SQL statements', N'equal', 1)
GO